Parsing HTML and XML in Web Workers
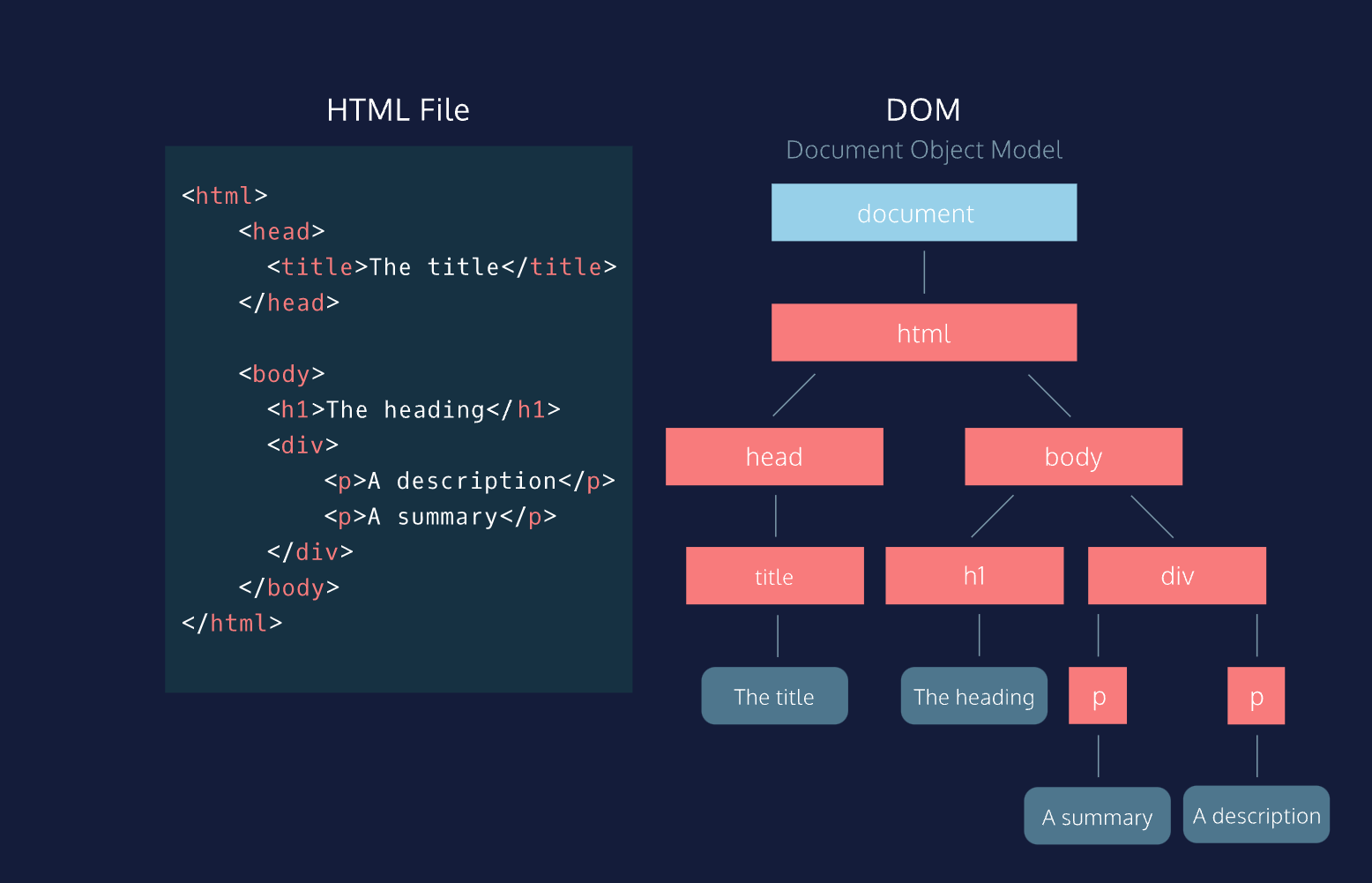
Introduction: Explaining the need for parsing HTML and XML data in web workers
Web workers are a powerful feature of modern web browsers that allow developers to run JavaScript code in a separate background thread, separate from the main thread that runs the web page's user interface. This provides a number of benefits, such as improved performance, better responsiveness, and reduced risk of freezing the user interface.
However, web workers have some limitations, such as the fact that they cannot directly access the Document Object Model (DOM) of the web page. This means that if you want to parse or manipulate HTML or XML data in a web worker, you need to use a different approach.
There are many cases where parsing HTML or XML data in a web worker is necessary. For example, if you are building a large web application that needs to process large amounts of data, you may want to offload some of that work to a web worker to keep the user interface responsive. Or, if you are working with an API that returns HTML or XML data, you may want to parse that data in a web worker before displaying it on the page.
Unfortunately, there are not many libraries that provide a way to parse HTML or XML data in a web worker. The standard DOMParser API is not available in web workers, and many popular parsing libraries are designed to work in a browser environment and rely on the DOM.
This is where XSDOMParser comes in. XSDOMParser is a lightweight and performant library that provides a way to parse and manipulate HTML and XML data in a web worker environment. It is built using regular expression tokenizations to provide fast and efficient parsing, and it provides a rich set of functionality for navigating and manipulating the resulting parse tree.
In the next sections of this article, we'll dive deeper into how XSDOMParser works and how you can use it to parse and manipulate HTML and XML data in a web worker environment.
Benefits of Parsing HTML and XML Data in Web Workers
Parsing HTML and XML data in web workers can provide a number of benefits, especially when working with large amounts of data or complex data structures. Let's take a closer look at some of these benefits.
1. Improved Performance
When you parse HTML or XML data in a web worker, you are offloading the parsing and processing work to a separate thread, which can improve performance and keep the user interface responsive. This is especially important when working with large data sets or complex data structures.
For example, let's say you are building a web application that needs to process a large amount of XML data. Without using a web worker, this could cause the user interface to freeze or become unresponsive. By parsing the XML data in a web worker, you can keep the user interface responsive and provide a better user experience.
Here's an example of how you can use XSDOMParser to parse XML data in a web worker:
// create a new web worker
const worker = new Worker('worker.js');
// send the XML data to the web worker
worker.postMessage(xmlData);
// listen for the result from the web worker
worker.addEventListener('message', event => {
const xmlDoc = event.data;
// do something with the parsed XML document
});
2. Improved Security
Parsing HTML or XML data in a web worker can also improve security by isolating the parsing and processing work from the main thread that runs the web page's user interface. This can help prevent cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks and other security vulnerabilities.
3. Flexibility
By parsing HTML or XML data in a web worker, you have more flexibility in how you process and manipulate the data. For example, you can use XSDOMParser to extract specific elements or attributes from the parse tree, or to modify the parse tree before displaying it on the page.
Here's an example of how you can use XSDOMParser to extract specific elements from an HTML document:
const parser = new XSDOMParser();
const htmlDoc = parser.parseFromString(htmlData, 'text/html');
// get all the anchor elements from the HTML document
const anchors = htmlDoc.querySelectorAll('a');
// do something with the anchor elements
Overview of XSDOMParser library
XSDOMParser is a lightweight and performant JavaScript library for parsing HTML and XML data in a web worker environment. It was developed to provide a way to parse and manipulate XML and HTML data in a separate thread, which can improve performance and keep the user interface responsive. In this section, we will provide an overview of the XSDOMParser library, including its key features and how it works.
Key Features
XSDOMParser provides a number of key features that make it a useful library for parsing HTML and XML data in web workers. Some of its key features include:
-
Lightweight: XSDOMParser is a lightweight library that does not require any external dependencies. It is designed to be fast and efficient, and to work well in a web worker environment.
-
Supports XML and HTML: XSDOMParser can parse both XML and HTML data, making it a versatile library for working with structured data.
-
Simple API: XSDOMParser provides a simple and easy-to-use API for parsing and manipulating XML and HTML data. It is designed to be easy to use, even for developers who are new to parsing XML and HTML data.
Installation of XSDOMParser in the Web Worker
The XSDOMParser library can be installed in a web worker using either npm or by downloading the source files directly. Once you have installed XSDOMParser, you can easily import it into your web worker script and start parsing XML and HTML data.
Using npm
To install XSDOMParser using npm, open your terminal and navigate to your project directory. Then, run the following command:
npm install xsdomparser
This will install the XSDOMParser library and add it to your project's dependencies. You can then import the library in your web worker script using an import statement:
import XSDOMParser from 'xsdomparser';
Using Source Files
If you prefer to install XSDOMParser by downloading the source files, you can do so by visiting the XSDOMParser GitHub repository and downloading the latest release.
Once you have downloaded the source files, you can include them in your web worker script using an import statement:
import XSDOMParser from './path/to/xsdomparser.js';
Note that the path to the XSDOMParser file may vary depending on where you have placed it in your project directory.
Example Usage
Here's an example of how to use XSDOMParser in a web worker script:
import XSDOMParser from './path/to/xsdomparser.js';
self.addEventListener('message', (event) => {
const parser = new XSDOMParser();
const xmlDoc = parser.parseFromString(event.data, 'text/xml');
// Manipulate the XML data as needed
const title = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName('title')[0].childNodes[0].nodeValue;
console.log(title); // Output: The Catcher in the Rye
// Send the parsed data back to the main thread
self.postMessage(title);
});
In this example, we create a web worker that listens for messages using the addEventListener method. When a message is received, we create a new instance of XSDOMParser and use the parseFromString method to parse the XML data into an XML document. We can then manipulate the XML data as needed using DOM methods. Finally, we send the parsed data back to the main thread using the postMessage method.
Note that this example assumes that you have created a separate JavaScript file for your web worker (worker.js). In practice, you may need to modify the code to fit the specific requirements of your project.
Parsing HTML or XML using XSDOMParser
Once you have installed XSDOMParser in your web worker, you can use it to parse XML and HTML data. The parse method is used to parse a string of XML or HTML data into an XML document.
Here's an example of how to parse an XML document using XSDOMParser:
import XSDOMParser from './path/to/xsdomparser.js';
const parser = new XSDOMParser();
const xmlString = '<book><title>The Catcher in the Rye</title><author>J.D. Salinger</author></book>';
const xmlDoc = parser.parse(xmlString, 'text/xml');
// Accessing the XML data using DOM methods
const title = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName('title')[0].childNodes[0].nodeValue;
console.log(title); // Output: The Catcher in the Rye
const author = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName('author')[0].childNodes[0].nodeValue;
console.log(author); // Output: J.D. Salinger
In this example, we create a new instance of XSDOMParser and pass it an XML string to parse using the parse method. We then use DOM methods to access the data within the XML document.
Similarly, here's an example of how to parse an HTML document using XSDOMParser:
import XSDOMParser from './path/to/xsdomparser.js';
const parser = new XSDOMParser();
const htmlString = '<html><body><h1>Welcome to my website</h1><p>Here is some content...</p></body></html>';
const xmlDoc = parser.parse(htmlString, 'text/html');
// Accessing the HTML data using DOM methods
const heading = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName('h1')[0].childNodes[0].nodeValue;
console.log(heading); // Output: Welcome to my website
const paragraph = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName('p')[0].childNodes[0].nodeValue;
console.log(paragraph); // Output: Here is some content...
In this example, we use the same process to parse an HTML string using XSDOMParser. We can then access the data within the HTML document using DOM methods.
Manipulating Parsed Data
Once you have parsed your XML or HTML data using XSDOMParser, you can manipulate the data to extract the information you need. This can be done using DOM methods to traverse the parsed document and select the desired elements.
Here's an example of how to manipulate the parsed data from the previous examples:
// Continuing from the previous example...
// Creating a new DOM element and adding it to the document
const newElement = xmlDoc.createElement('genre');
const textNode = xmlDoc.createTextNode('Fiction');
newElement.appendChild(textNode);
xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName('book')[0].appendChild(newElement);
Similarly, here's an example of how to manipulate the parsed data from an HTML document:
// Continuing from the previous example...
// Changing the text of an HTML element
xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName('h1')[0].childNodes[0].nodeValue = 'Hello World';
// Serializing the document back to a string
// Output: "<html><body><h1>Hello World</h1><p>Here is some content...</p></body></html>"
How XSDOMParser is built
XSDOMParser is a library that provides a simple and efficient way to parse HTML and XML data in a web worker. In this section, we'll dive into how XSDOMParser is built and how it works.
Unlike the DOMParser API, which is not available in web workers, XSDOMParser is built using regular expression tokenizations to parse and traverse HTML and XML data. This allows XSDOMParser to be lightweight and performant, while still providing a rich set of functionality for parsing and manipulating HTML and XML data.
The core of XSDOMParser is its tokenizer, which takes in raw HTML or XML data and breaks it down into a series of tokens that can be easily processed and manipulated. XSDOMParser's tokenizer is built using regular expressions to match different types of tokens, such as tags, attributes, and text nodes.
Here are some examples of regular expression tokens used by XSDOMParser:
- tagRegExp: This regular expression matches opening and closing HTML or XML tags, and captures the tag name and attributes. Here's an example:
const tagRegExp = /<(\/)?([a-z]+)([^>]*)?>/gi;
const html = '<div class="example">Hello, world!</div>';
const match = tagRegExp.exec(html);
console.log(match[1]); // undefined
console.log(match[2]); // 'div'
console.log(match[3]); // ' class="example"'
- attributeRegExp: This regular expression matches HTML or XML attributes, and captures the attribute name and value. Here's an example:
const attributeRegExp = /([a-z]+)=(["'])(.*?)\2/gi;
const html = '<div class="example" data-id=\'123\'>Hello, world!</div>';
const match = attributeRegExp.exec(html);
console.log(match[1]); // 'class'
console.log(match[3]); // 'example'
Once the tokenizer has broken down the HTML or XML data into tokens, XSDOMParser builds a parse tree using these tokens. The parse tree is a hierarchical representation of the HTML or XML data, with each node in the tree representing a tag, attribute, or text node.
With the parse tree in place, XSDOMParser provides a set of methods for traversing and manipulating the tree. These methods allow developers to easily navigate the tree, find specific nodes, modify node attributes, and more.
One of the key benefits of XSDOMParser's approach to parsing and traversing HTML and XML data is that it is fast and efficient, even when dealing with large amounts of data. Because XSDOMParser uses regular expression tokenizations, it can quickly process HTML and XML data without the performance overhead of more complex parsing algorithms.
If you're interested in using XSDOMParser in your own projects, you can find the source code and documentation on the project's GitHub repository: https://github.com/lexmihaylov/XSDOMParser.
